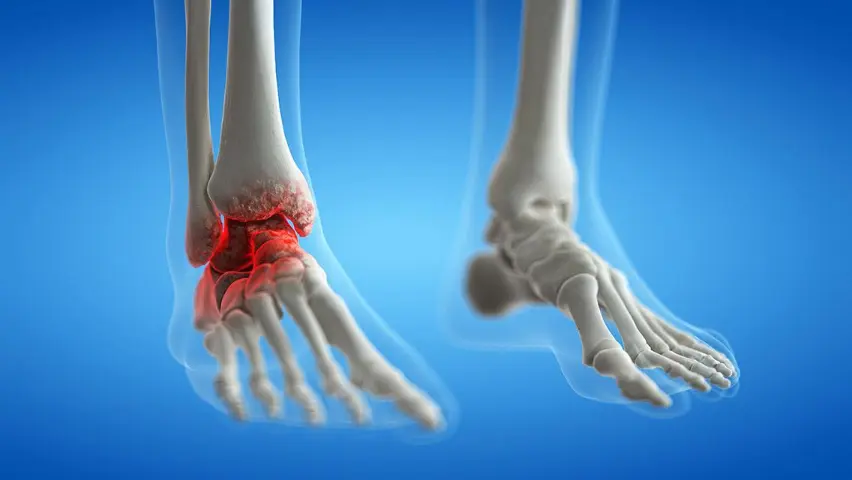
Degenerative Joint Disease Leading to Pain and Stiffness in the Ankle
What Is Ankle Arthritis?
Ankle arthritis refers to the breakdown of cartilage in the ankle joint, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Unlike the knee or hip, the ankle is less commonly affected by arthritis, but when it occurs, it can be equally debilitating. The most common type is post-traumatic arthritis, which often develops after previous ankle injuries, though osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) can also affect the joint.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Previous ankle fractures or severe sprains
- Chronic ligament instability
- Inflammatory conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Genetic predisposition to joint degeneration
- Age-related wear and tear (less common than in other joints)
- Infection or septic arthritis
- Obesity or repetitive impact loading
Symptoms
- Pain with weight-bearing or prolonged standing
- Swelling around the ankle joint
- Joint stiffness, especially in the morning or after rest
- Reduced range of motion
- Grinding or catching sensations in the joint
- Visible deformity or misalignment in advanced cases
Diagnosis
- Physical examination assessing pain, joint mobility, and alignment
- X-rays to evaluate cartilage loss, joint space narrowing, and bone spurs
- MRI for soft tissue assessment and early cartilage degeneration
- CT scan for surgical planning in advanced cases
Treatment
Non-Surgical Treatment
- Activity modification and weight management
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Ankle braces or supportive footwear
- Physical therapy to maintain mobility and strength
- Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections for temporary relief
Surgical Treatment
- Arthroscopic debridement: For mild arthritis, removing loose cartilage or bone fragments
- Ankle fusion (arthrodesis): Permanently joins the bones to eliminate pain, ideal for younger, active patients
- Total ankle replacement: Preserves motion in the joint; considered for low-demand patients with advanced arthritis
- Realignment procedures (osteotomies): Shift load away from the arthritic part of the joint
Recovery Timeline
- Conservative treatment may require ongoing management over months or years
- Post-surgical recovery varies:
- Arthroscopic debridement: 4–6 weeks
- Ankle fusion: 8–12 weeks of non-weightbearing followed by gradual rehab
- Ankle replacement: 12–16 weeks with gradual return to function
- Full return to activity depends on procedure type and individual progress
Expert Treatment at Kerlan Jobe Institute
At Kerlan Jobe Institute, we offer personalized treatment for ankle arthritis, from conservative care to advanced surgical interventions. Our orthopedic specialists work closely with each patient to preserve mobility, reduce pain, and improve long-term quality of life.